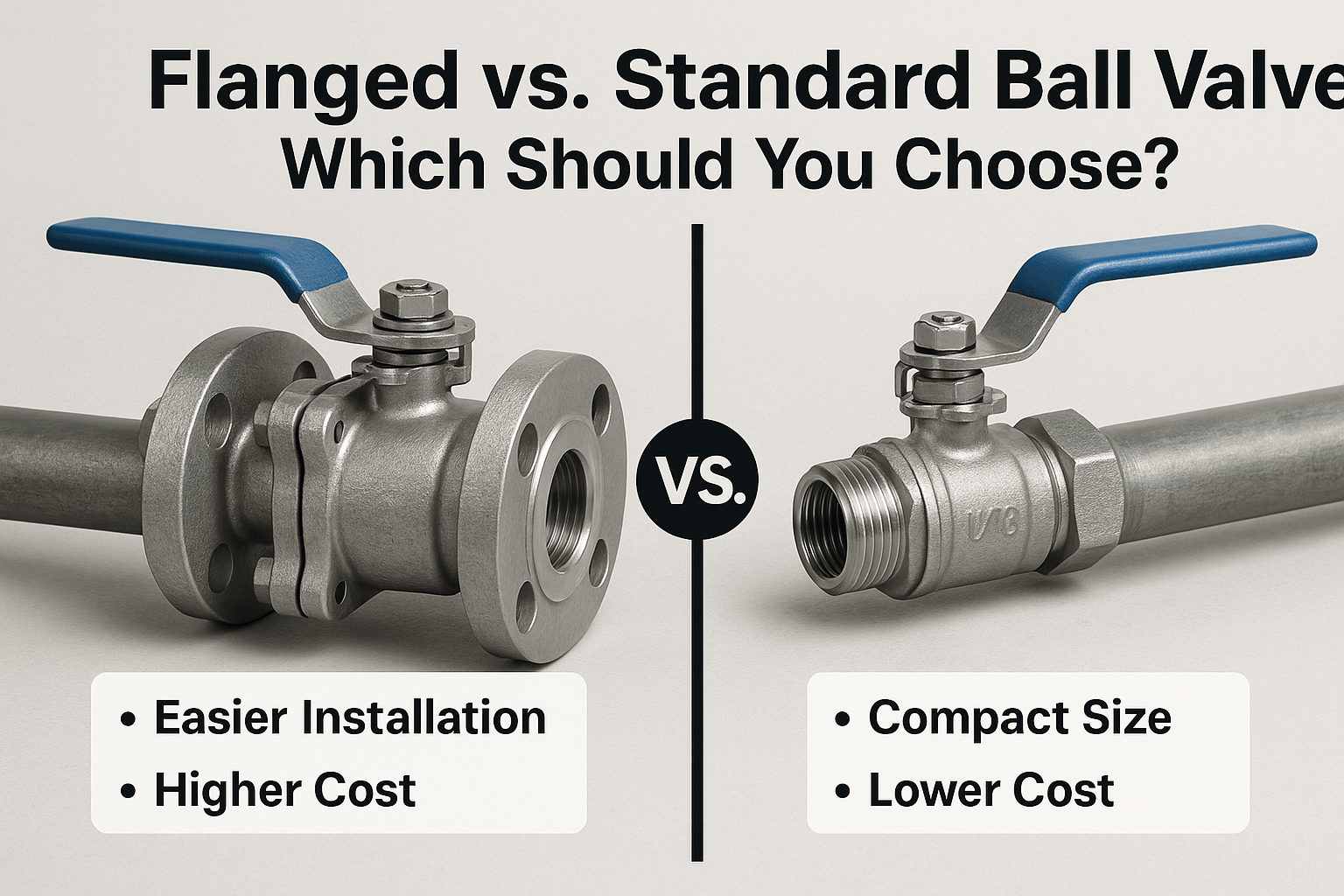
In industrial piping systems, ball valves are a necessary component that allow fluid or gas flow control with precision and reliability. However, they're not all made the same. One of the most common questions in selecting the right type ball valve for an application is flanged vs. standard ball valve. This choice can significantly alter how the system performs, how it is installed, how it is maintained, and the overall safety to operate it.
Flanged ball valves have flanged ends that are bolted to flange connections on a pipeline. Standard ball valves typically are either threaded or welded for their end connections allowing their use for slightly different installation and pressure conditions. By identifying the benefits and drawbacks of each type will allow you to order with confidence for your application whether it is a chemical processing plant, water distribution system, or dealing with a gas handling system. Let's take a further look at valve comparison of both valve types and discuss differences to allow you to choose the best option.
Flanged ball valves are meant for specific ends with bolts colliding on a pipe-flanged connection. They are accurately designed for large-scale piping, extremely high operating pressure, or conditions where regular maintenance or inspection is preferred. The flanged ends provide connections that are easily disassembled without cutting the pipe while possessing strength, stability, and tight sealing against leaks.
On the other hand, ball valves, in general, are fitted with ends that are either threaded (screwed) or welded. Threaded ball valves are usually found on smaller pipe systems and may be used on lower-pressure systems. Welded ball valves would provide permanent tamper-proof attachment that is very suitable for a high-pressure system where the amount of leak points must be kept as low as possible.
A vital aspect that differentiates flanged and regular ball valves is the installation method. Flanged valves can be easily unscrewed from their flanges when they have to be replaced, this favors a quick installation procedure and facilitates repeated maintenance and inspection Their strong connection is more likely to be leak proof even when the pressure is high, so they are highly suitable fit for high pressure systems.
In general, standard ball valves, especially those threaded, are cheaper and available at a quicker initial installation. However, for their removal, the pipeline may need to be cut, making maintenance more labor-intensive. Welded ball valves are perfect leaks. Once they are in place, removal or replacement of the valve entails cutting the pipe and repairing it with a weld, adding to the costs and downtime.
Flanged and standard ball valves are both manufactured from various materials including stainless steel, brass, carbon steel, and PVC. Their material construction depends on their applications and nature of pipeline systems. Flanged ball valves are standardly used in industries such as oil and gas, chemical processing, and power generation where reliability of the systems is very essential and the fluid media may be corrosive or hazardous.
Threaded or welded types are more acceptable in domestic plumbing, small industrial systems, and instrumentation applications. These environments generally have a lower frequency of maintenance and have low pressure or temperature requirements.
Flanged ball valves are better from a safety standpoint, as they are designed with more structural integrity and can handle greater pressures and temperatures. The flanged joints offer a positive seal, which minimizes leakage potential under varying pressure, and can greatly reduce the risk of leaking or rupturing a system that is conveying highly dangerous and/or high-temperature materials.
A standard ball valve with a threaded connection can wear over time, especially in vibrating or thermally cycled systems. Because a welded valve has eliminated threaded joints, it does not have the fault of wear. However, it has additional challenges to safety inspections and emergency repairs since it is not removable.
In general, single flanged ball valves are usually rated higher in pressure than standard threaded valves. Welded valves are another worthy alternative to use in high pressure systems but the downside is that they have a complex design which makes repairs not as easy.
|
Feature |
Flanged Ball Valves |
Standard Ball Valves (Threaded/Welded) |
|
Connection Type |
Bolted flanges |
Threaded (screwed) or welded ends |
|
Ease of Installation |
Moderate difficulty as alignment of flanges and bolts is necessary. |
High difficulty for threaded ; Low difficulty (welded due to permanent installation) |
|
Maintenance |
Easy hassle-free removal for inspection and servicing |
Threaded: moderately easy removal Welded: difficult and requires much effort and time. |
|
Leak Resistance |
Failproof due to secure flange bolts |
Threaded: Moderate risk is there. Welded: Excellent |
|
Cost |
Cost more |
Cheap (threaded), Medium to high (welded) |
|
Durability Under Pressure |
Perfect fit for high-pressure applications |
Threaded: low to medium durability, Welded: solid and robust durability. |
|
Common Applications |
Industrial systems, chemical, oil and gas pipelines |
Plumbing, HVAC, smaller processing units |
|
Pipe Size Suitability |
Ideal for medium to large-diameter pipes |
Threaded: small to medium; Welded: small to large |
|
Installation Time |
Longer due to bolting procedure |
Threaded: quick; Welded: time-intensive |
|
Reusability |
Highly reusable |
Threaded: reusable; Welded: non-reusable |
So, flanged or standard ball valves; what's the decision? It depends on the operational conditions of your system, your maintenance needs and any budget constraints you have.
Flanged ball valves should be your choice when your best operational requirements include high-pressure fluids, the operational needs include regular inspection, or if it is mission-critical.
If you are dealing with high-pressure fluids, and the piping system requires regular inspections, then flanged ball valves are the best fit because they offer a safe and sustainable connection that provides high performance when put under stress, easy access for repairs and adjustments, and are much more secure.
In case of a residential plumbing system, or a low-pressure plumbing system or a makeshift install solution, a standard threaded ball valve can offer is an inexpensive and feasible option promising a quicker install option. If you are working with high-pressure pipelines where having a leak-proof connection is important and you do not think you will have to disassemble the valve you can use a welded ball valve.
The decision to use a flanged or standard ball valve depends mainly on the operational requirements of the system. There is no absolute answer. Flanged valves bring strength, serviceability and reliability; standard valves (threaded or welded) offer flexibility, less up-front costs and simpler installation in many cases.
Industries must continually update their operations to achieve the best output. Not staying activ...
READ FULLThe valve system consists of various kinds of components, and actuators are one of them. When it ...
READ FULLValves need support from an electric system that can control them remotely. Not every time and pl...
READ FULL